Entrust your samples to Cryosite for unparalleled options in harnessing today's treatments and future research breakthroughs through top-tier umbilical cord blood storage.
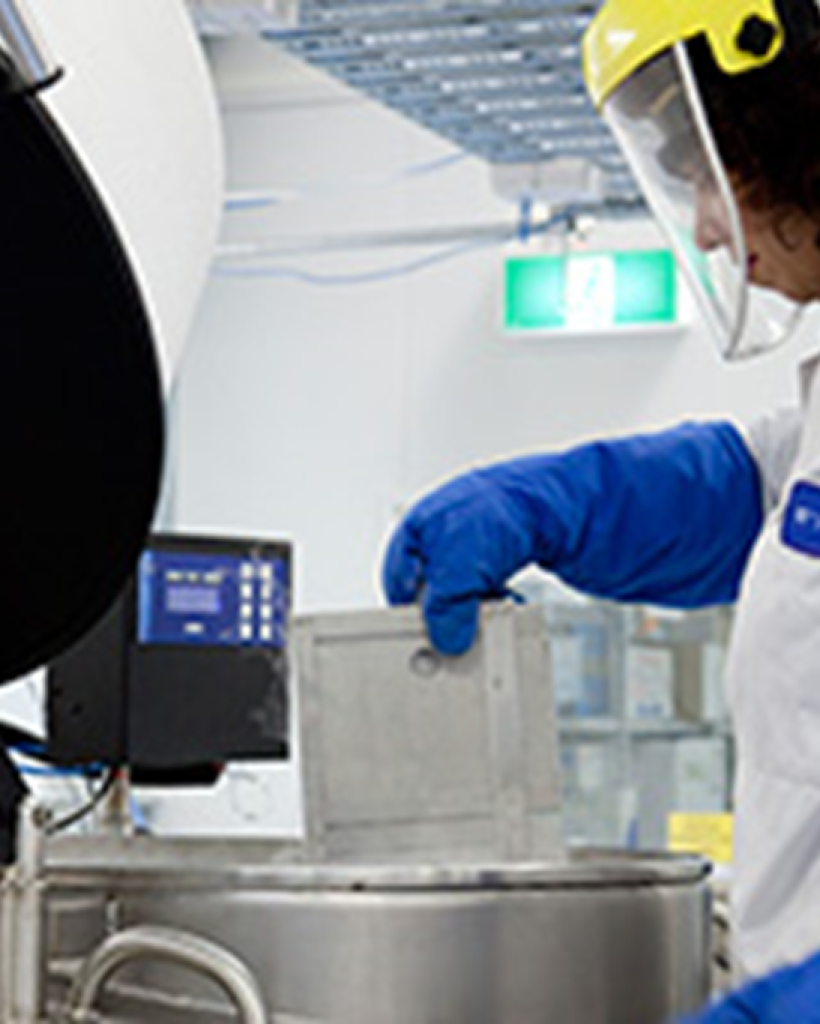

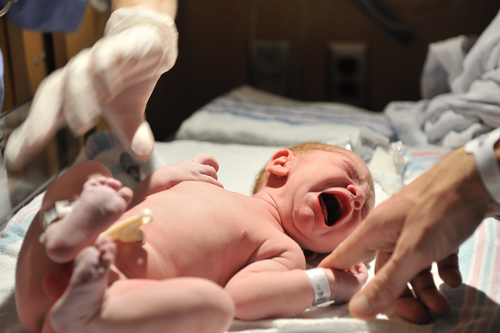
Cryosite ceased collection and storage of new cord blood/tissue samples in 2017. We’re committed to preserving cord storage for samples collected and processed by Cryosite before this period.
Cryosite, pioneering cord blood banking since 2002, was the first licensed private cord blood bank in Australia. A trusted leader in clinical trial samples and cord blood storage.
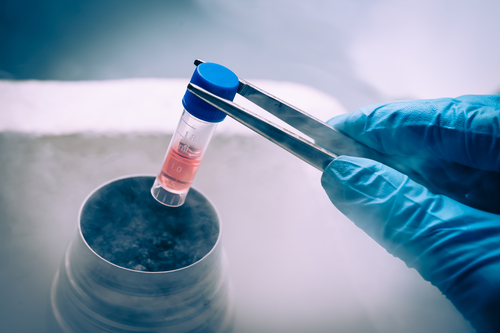
Cryosite uses state-of-the-art technology, quality management systems and a highly experienced team to maintain the value of stored samples in our fully monitored facility.
A baby’s umbilical cord contains blood and tissue, which are rich sources of therapeutic stem cells.
Stem cells are special because they can divide and make exact copies of themselves and develop into other specific cell types, tissues or organs in the body. Cord blood and cord tissue are used as sources of different types of stem cells.
Cord blood/tissue samples are a unique 100% match to the individual from whom they are collected and cannot be replaced.
Samples may provide future treatment options for immediate family members; parents have a partial match and siblings have a potential match.
Cord blood banking helps our clients safeguard their families' future health outcomes by storing cord blood and tissues, ensuring they take an important step in protecting their loved ones.
Cord blood is a source of haematopoietic stem cells, which can produce blood cells that carry oxygen, fight infection and stop bleeding.
A cord blood sample, gathered at birth, offers greatly increased options and benefits in the treatment of over 80 diseases—including leukemias, blood diseases and lymphomas—compared to synthetic or donated stem cells.
Cord tissue contains several cell types that can produce many different types of cells including bone, cartilage, muscle.
Current research explores bone conditions, heart disease, graft-versus-host disease in donor marrow transplantation, and autoimmune responses in multiple sclerosis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Cord blood banking offers hope for these advancements, potentially transforming treatment options and patient outcomes.
Over 1000 clinical trials around the world are currently recruiting patients to investigate the further potential of stem cell transplants and future use in regenerative medicine.
New technology will also allow development of stored stem cells to the next generation of advanced cell therapies and personalised treatment.
Stem Cells Australia has an interesting summary of current Australian Stem Cell Research projects.
While the potential of stem cell therapies is exciting, it is important to note that current approved uses are limited, results are variable and future uses are developing in clinical trials. The decision to use stem cells should be made with a cellular therapy professional.
Cryosite ensures top-notch umbilical cord blood storage in a secure facility with cutting-edge equipment for peace of mind.
Take a virtual tour of our laboratory.
Former StemLife customer samples were acquired by Cryosite in 2016.
Cryosite is dedicated to the long-term cord storage of all StemLife cord blood samples. Our state-of-the-art facility ensures your family's peace of mind, knowing these precious samples are securely stored and protected for the future.
Cryosite are the pioneers for private cord blood storage in Australia and we have been trusted to store cord blood/tissue samples since 2002.
The Cryosite team includes highly experienced and qualified scientists who are dedicated to keeping cord blood/tissue samples secure.

Contact Our Dedicated Team
Cryosite are the pioneers for private cord blood storage in Australia and we have been trusted to store temperature-sensitive samples since 2000.

Cryosite was established with the specific objective of providing specialised clinical trials depot services to a wide range of clients from the research, medical, pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries.
In the highly regulated, complicated, clinical trial environment, our mission is simple: we take care of your warehousing, distribution and logistics needs so you can concentrate on your core objectives.
Cryosite acknowledges the Traditional Owners of the land, sea and waters of the area on which we live and work. We acknowledge the Darug peoples’ continuing connection to culture and pay our respects to Elders past and present.